Vector vs Raster Differences
Essential knowledge for laser processing data creation: understanding the difference between vector and raster.
📌 Target Audience and Terminology This article assumes CO₂ laser processing machines (40W-80W range). “Vector format/Raster format” refers to data formats, while “Vector processing/Raster processing” refers to processing methods.
Basics of Vector and Raster Formats
| Vector Format | Raster Format | |
|---|---|---|
| Data Structure | Points, lines, paths digitized (expressed by coordinates) | Collection of very small squares (pixels) |
| Enlargement/Reduction | Borders remain smooth even when enlarged | Outlines become jagged when enlarged |
| File Extensions | SVG, EPS, AI | PNG, JPG, GIF, BMP |
| Software | Inkscape (free), Illustrator, etc. | GIMP (free), Photoshop, etc. |
| Good for | Text, shapes, illustrations and icons, logos | Photos, images with subtle color gradations |
Differences in Laser Processing
| Vector Processing | Raster Processing | |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Processing | Cutting & Engraving | Engraving Only |
| Laser Head Movement | Processes by tracing indicated lines (paths) | Processes by repeating horizontal scanning in X-axis direction |
| Laser Light Output | Continuous irradiation from start to end point | Spot irradiation per pixel |
| Processing Time | Short time due to efficient movement | Takes time as entire surface is scanned |
| Suitable Work Examples | Shape cutting, text cutouts | Photo engraving, works requiring gradation or shading expression |
Vector processing moves like drawing in one stroke from path start to end point, characterized by efficiency and short processing time. Raster processing reciprocates from left to right, scanning the entire surface, so it takes time.
Laser Head Movement Differences:
| Vector Processing | Raster Processing | |
|---|---|---|
| Line Processing | 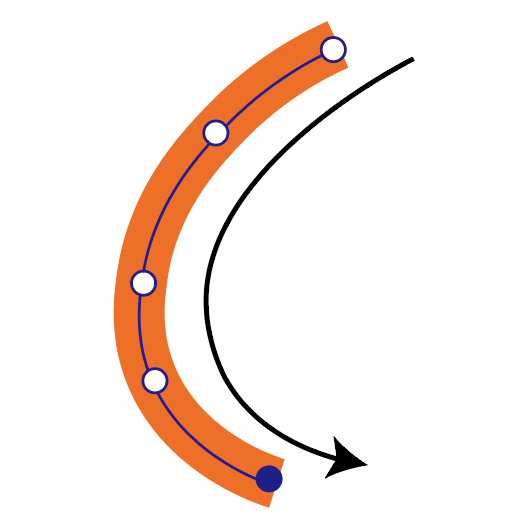 | 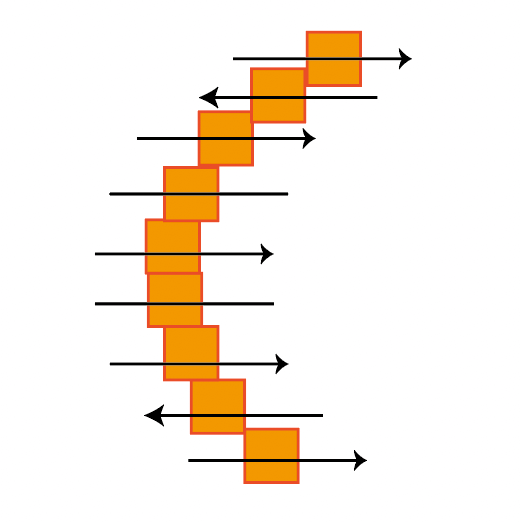 |
| Shape Processing | 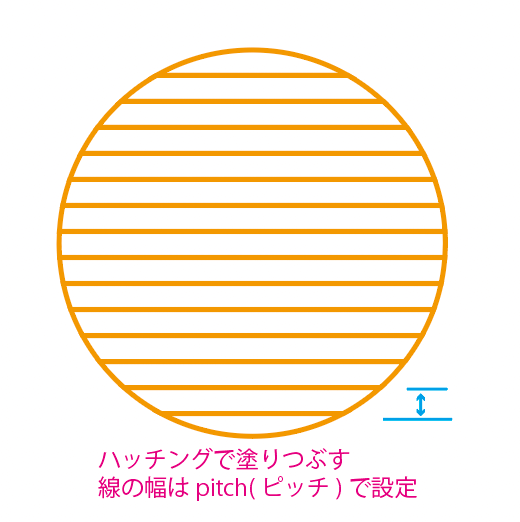 | 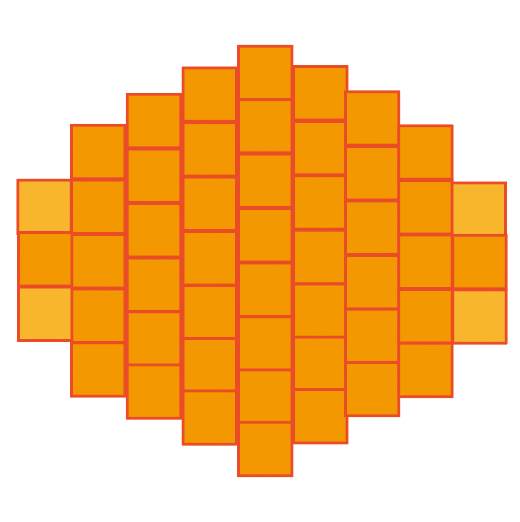 |
Common Beginner Mistakes
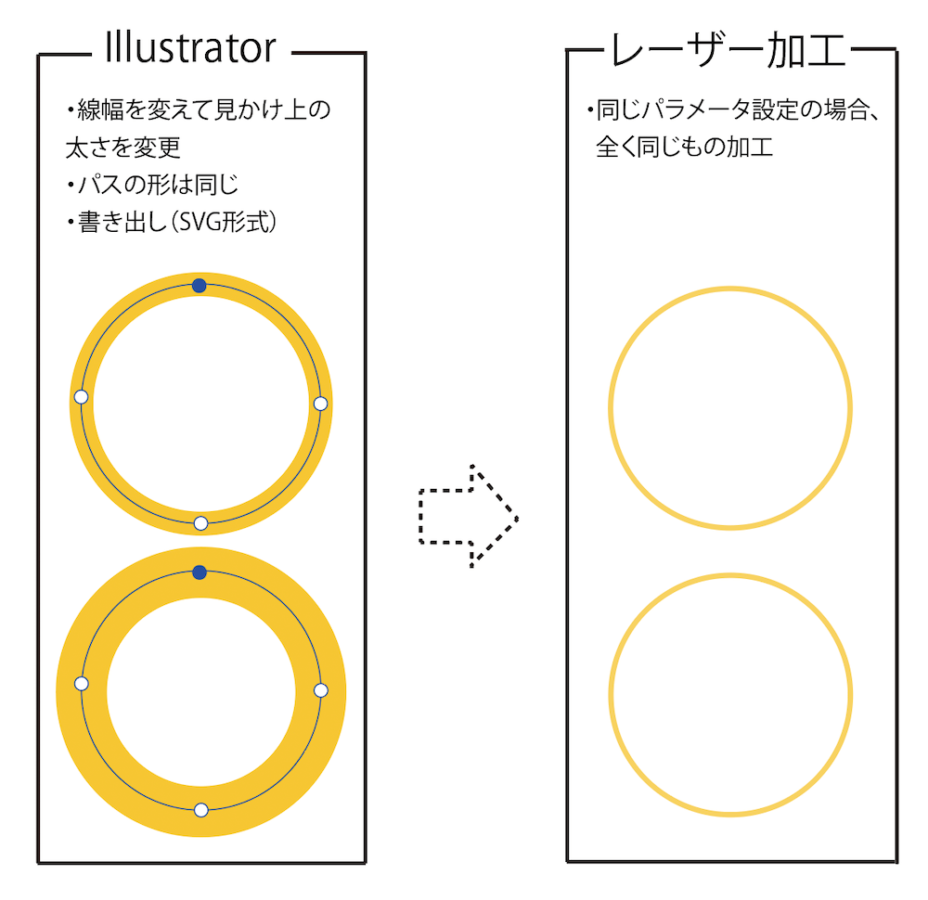
① Thinking Changing Line Width Makes Processing Thicker [Most Important]
- Wrong: Making line width thicker in drawing software makes laser processing thicker
- Correct: In vector processing, the laser irradiates along the path (line center). Changing line width doesn’t change actual processing width (kerf)
- Solution: To create thick lines, arrange multiple paths in parallel or adjust laser output/speed
② Overlooking Duplicate Paths (Double Lines) [Dangerous]
If multiple paths overlap in the same location, the laser processes the same spot multiple times, causing material to scorch or create fire risk.
Confirmation method: Select all (Ctrl + A) → View → Outline (Ctrl + 5) to check for duplicates
③ Lines Too Thin or Spacing Too Narrow
Recommended values (40W-80W CO₂ laser guideline):
- Minimum line width: 0.3mm or more
- Minimum spacing: 0.7mm or more
⚠ Important: Values vary by machine and material. Always confirm with test cuts.
④ Forgetting to Convert Text to Paths
If text isn’t converted to paths, fonts may be replaced and character shapes may collapse.
Conversion procedure: Select text → Path → Object to Path (Shift + Ctrl + C)
⑤ Mixing Raster and Vector
Cutting requires vector paths. Image lines (raster) cannot be cut.
Free Data Creation Software
| Software Name | Purpose | Suitable for Laser Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Inkscape | Vector Graphics | ◎ Essential for cutting |
| GIMP | Raster Image Editing | △ For photo engraving |
| Krita | Illustration (Raster) | △ For art-type engraving |
How to choose:
- Need cutting → Inkscape essential
- Photo engraving → GIMP
- Hand-drawn style → Krita
Points for Data Creation in Inkscape
Basic Settings
| Item | For Cutting | For Engraving (Vector) |
|---|---|---|
| Line Width | 0.1-0.3mm | None |
| Color | RGB red (255, 0, 0) | - |
| Fill | None | RGB black (0, 0, 0) |
💡 Tip: You can set different parameters for each color. Support varies by machine, so check your manual.
Checklist
- Text converted to paths (Shift + Ctrl + C)
- Cut lines are 0.1-0.3mm
- No duplicate paths (check with Ctrl + 5)
- Line spacing is 0.7mm or more
- Cut and engraving are color-coded
- Saved in SVG format
Summary
Key Points:
- Vector processing: Irradiates along paths (cutting & engraving)
- Raster processing: Irradiates via reciprocating scan (engraving only)
- Changing line width doesn’t change processing width
- Always convert text to paths
- Watch for duplicate paths (fire risk)
